In virtually any organization, controlling revenue is vital for sustainable development and financial stability. The revenue routine encompasses the entire method from the first customer conversation to the final number of payment. It involves different stages and actions that fundamentally determine the financial wellness of the organization. In this informative article, we shall examine the revenue cycle in more detail, discussing its key components, difficulties, and strategies for optimizing economic performance.
Introduction to the Revenue Pattern:
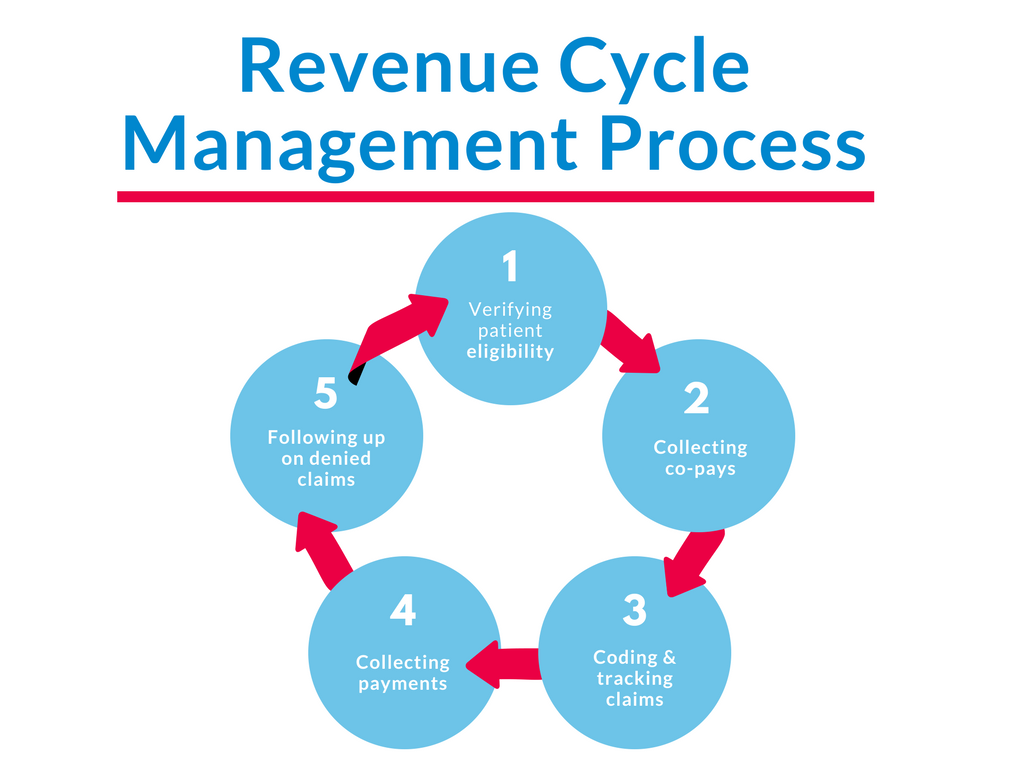
The revenue cycle shows the trip of revenue era in a organization. It generally begins with cause technology and advertising attempts and advances through revenue, order control, invoicing, cost series, and reconciliation. Each period in the revenue cycle represents a crucial position in ensuring accurate physician credentialing timely revenue recognition.
Key Components of the Revenue Routine:
a. Lead Era and Marketing: Attracting potential customers and creating recognition about services and products or services.
b. Sales and Customer Acquisition: Transforming leads in to customers through successful income methods and negotiations.
c. Buy Processing and Satisfaction: Obtaining and handling client requests, ensuring accurate item supply or support fulfillment.
d. Invoicing and Billing: Generating invoices for products or services rendered, including ideal pricing and terms.
e. Accounts Receivable Management: Tracking and obtaining exceptional from consumers, handling credit terms and cost terms.
f. Revenue Recognition and Revealing: Recognizing revenue predicated on accounting principles and rules, ensuring correct financial reporting.
Challenges in the Revenue Cycle:
Managing the revenue pattern effectively isn’t without their challenges. Some typically common challenges include:
a. Incorrect Data and Documentation: Incomplete or wrong data may lead to delays in invoicing and payment collection.
b. Billing and Development Problems: Mistakes in billing or development can lead to cost rejections or setbacks, impacting cash flow.
c. Appropriate and Effective Interaction: Not enough clear communication between departments can cause setbacks or misunderstandings in the revenue cycle.
d. Complex Cost Methods: Coping with varied payment practices, processing costs, and reconciling transactions can be time-consuming and error-prone.
e. Compliance and Regulatory Needs: Adhering to industry-specific rules and sales criteria could be complicated and require continuing monitoring.
Strategies for Optimizing the Revenue Period:
To maximize economic achievement and assure a smooth revenue cycle, businesses may implement the following techniques:
a. Streamline Techniques: Recognize bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the revenue pattern, and streamline processes to cut back delays and improve productivity.
b. Embrace Engineering: Implement powerful revenue period administration computer software and automation resources to enhance precision, speed, and efficiency.
c. Increase Information Reliability: Spend money on information validation and quality get a handle on measures to minimize problems and discrepancies in client data and billing details.
d. Increase Interaction and Venture: Foster effective transmission and collaboration between divisions involved in the revenue pattern to reduce misunderstandings and delays.
e. Monitor Crucial Efficiency Signs (KPIs): Establish and monitor appropriate KPIs such as for example times revenue excellent (DSO), selection costs, and revenue development to calculate and improve financial performance.
f. Staff Teaching and Training: Provide ongoing instruction and knowledge to personnel involved in the revenue period to ensure a deep comprehension of processes, submission, and most readily useful practices.
Conclusion:
The revenue routine is an essential facet of financial management and organizational success. By understanding the important thing parts, difficulties, and utilizing effective strategies, organizations may optimize their revenue pattern, enhance cash flow, increase client satisfaction, and achieve long-term economic stability. Constant monitoring, version to industry changes, and a responsibility to process improvement are important for agencies to thrive in today’s competitive company landscape.
